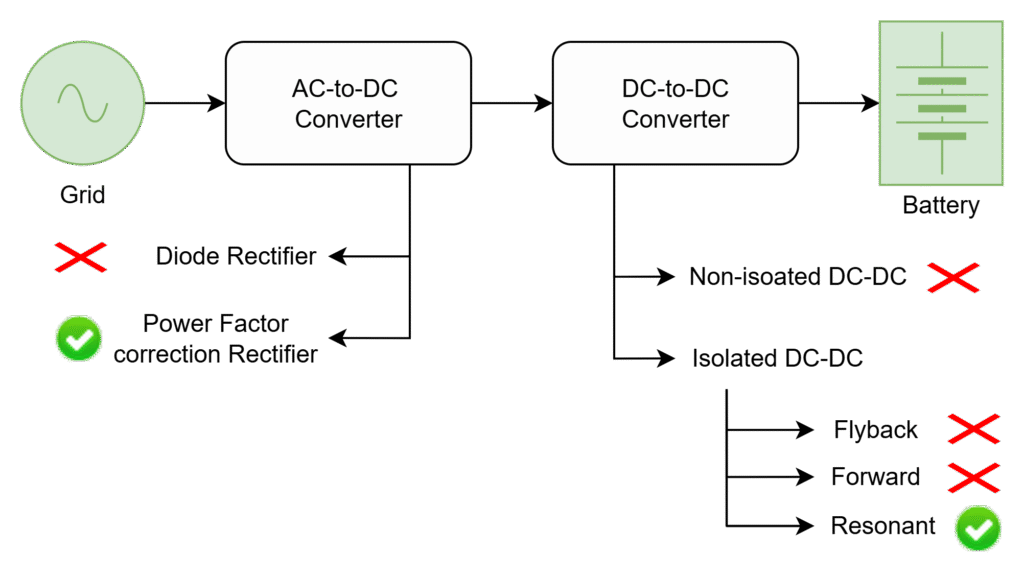
EV charger (either it is on-board or off-board) mainly consist of two power modules as shown below
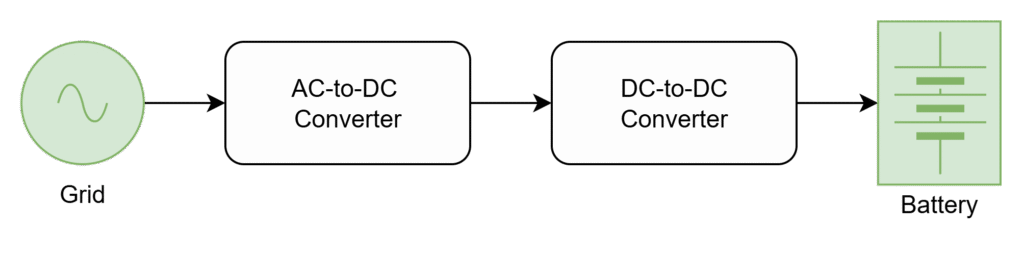
- AC-to-DC Converter (Rectifier)
- DC-to-DC Converter (Step-up/down)
Any electrical system/module primary requires,
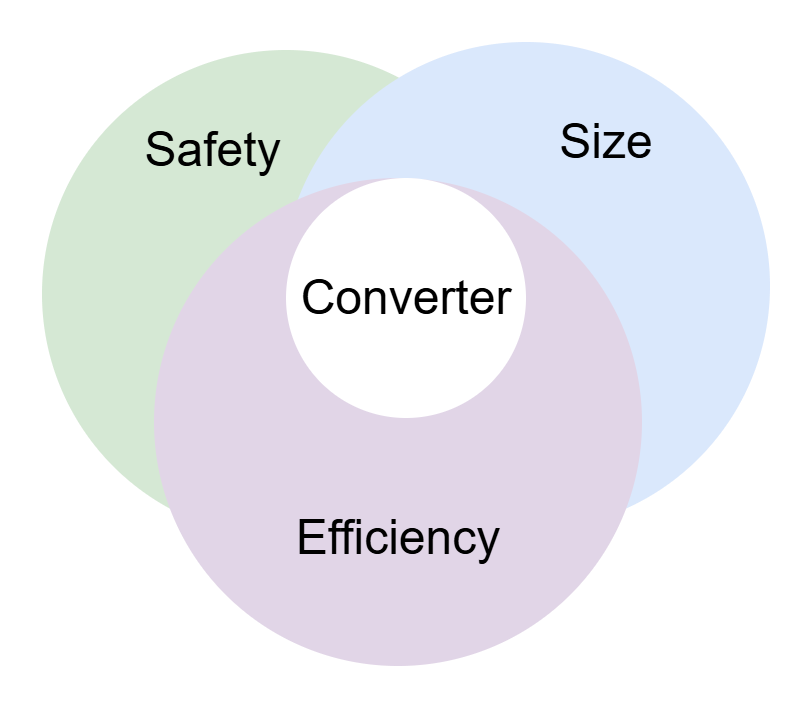
- Safety
- High power density (small size)
- High Efficiency
Grid is an AC source, battery is a DC source. To charge the battery AC should be converter into DC for that purpose, AC – DC converter is must. The rectified voltage can not be connected directly with the battery due to the potential differences of battery and rectified voltage. Hence a DC-DC converter is required.
Also, in any electrical systems, safety is primary that means isolation. DC-DC converter provides an isolation between the load and source.
Therefore, AC-DC and DC-DC converters are power modules of any type of EV charger.
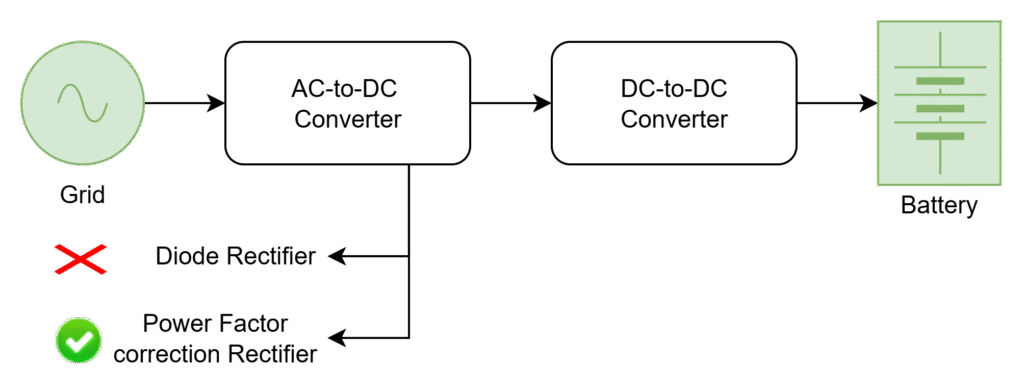
Diode rectifier is a basic AC- DC converter which converts the AC into DC form. But using this, the power quality which is drawing from grid is low due to low power factor and high harmonics. Hence, power factor correction rectifiers which can be drawn power with high power factor and low harmonics.
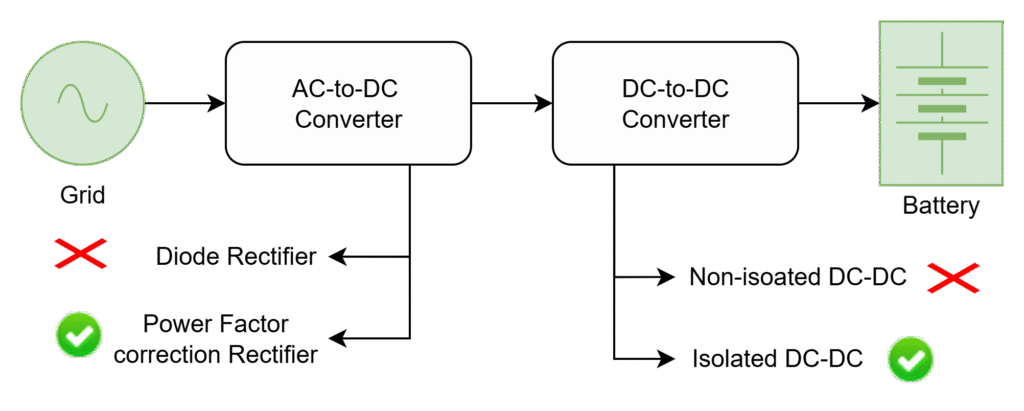
The isolated DC-DC converters provides the isolation between the source and load. But non-resonant isolated converters (PWM Converters Vs Resonant Converters) not support high-frequency operation due to switching losses. Resonant converters can operate at high-frequencies with reducing the switching losses.
Due to high switching frequency operations, magnetic components size reduces. Hence, system power density increases.
Due to resonance operation, switching losses reduces. Hence, system efficiency improves.
Power factor correction rectifiers:
- High power faxctor
- Power Quality increases
- Less harmonics
- High Efficiency
Resonant DC-DC converters:
- High frequency operation
- Small Size
- Low Losses
- Thermal Improvement
- High Efficiency
Leave a Reply