Two different areas are involved in any core shape
- Cross-sectional area, AE
- Window area, AW
These two areas multiplication only area product (AP = AE. AW) which is important and used in inductor design steps.
After selecting the core in magnetics design, we look for core areas in core data sheet for calculating the area product.
The core cross-sectional area (Ae) is directly available from core data sheet shown below
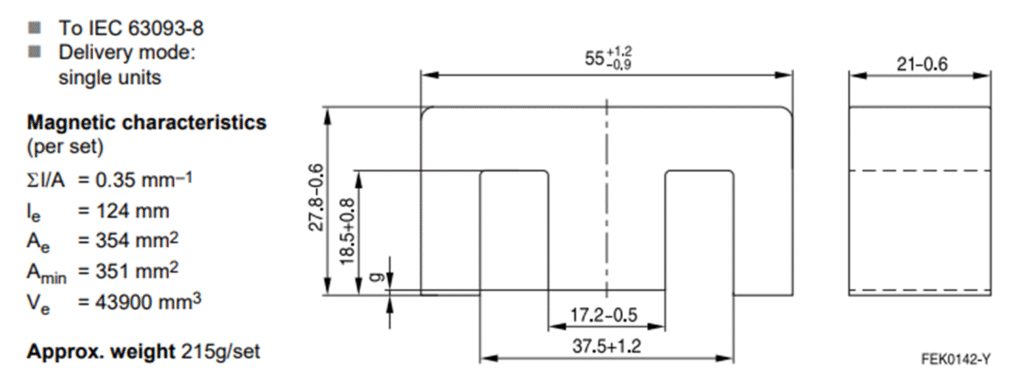
But the window area is not directly available from datasheet, it needs to be calculated based on dimensions given in datasheet or physical measurements of particular core. This calculation is different for various core shapes.
The mostly used core shapes are: EE , EI, UU, UI, Toroidal
Core Window Area (AW): The area which is used/available in core for winding the copper conductor/wire and insulations.
Let’s see how window area can be calculated for different core shapes based on given dimensions in core datasheet.
EE core shape
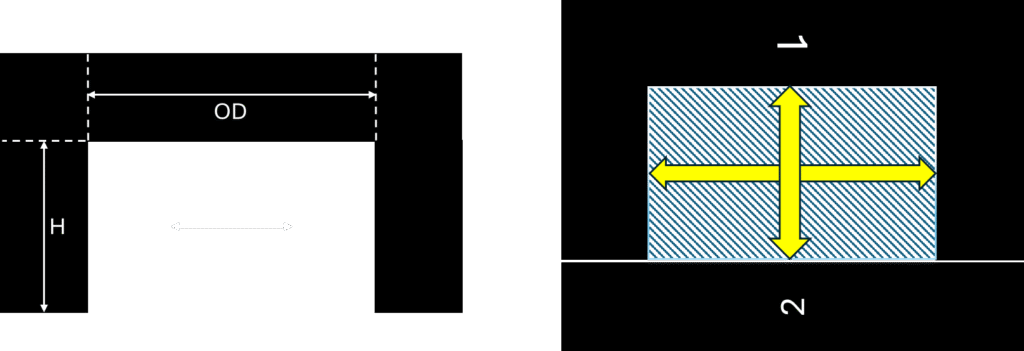
This is one of the most used core shape. The dimensions of E core will be given like this in any core data sheet like
Outer diameter – OD
Inner diameter – ID and
height – H
Any core should be closed for flux rotation, since this is EE shape, E-core will close core with another E-shape core.
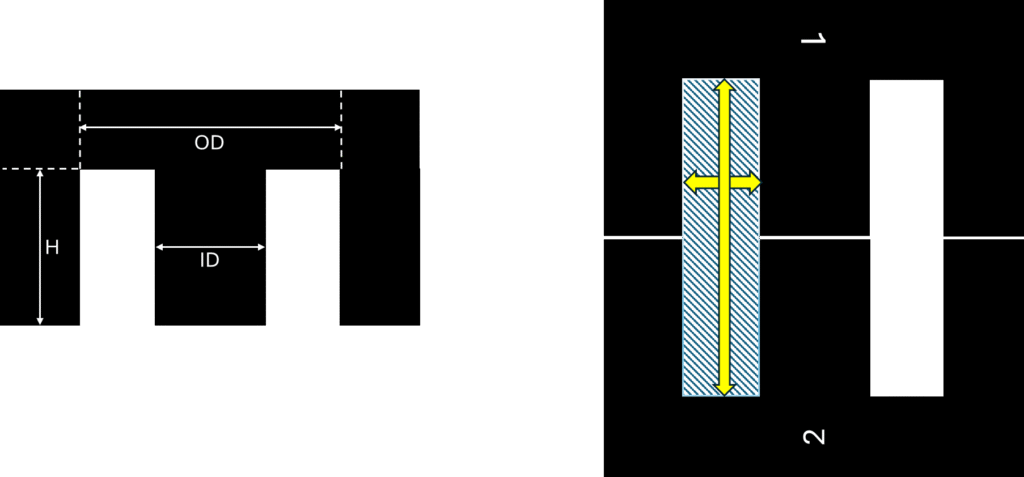
Here this is window area, area of any rectangular shape is multiplication of width and height
Width of core,
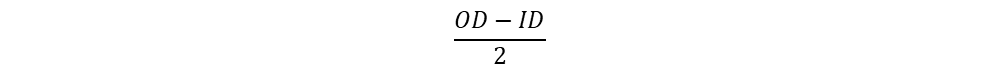
height of core, since we are using two Es, overall core height will be doubled
2H
Window area of EE shape core:
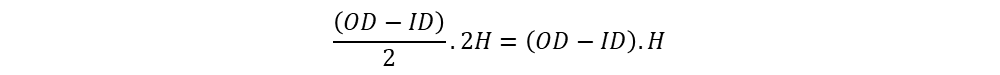
EI Core
In this, instead of ‘E’ shape core, ‘I’ shape bar will come in closing position as name suggesting as shown below
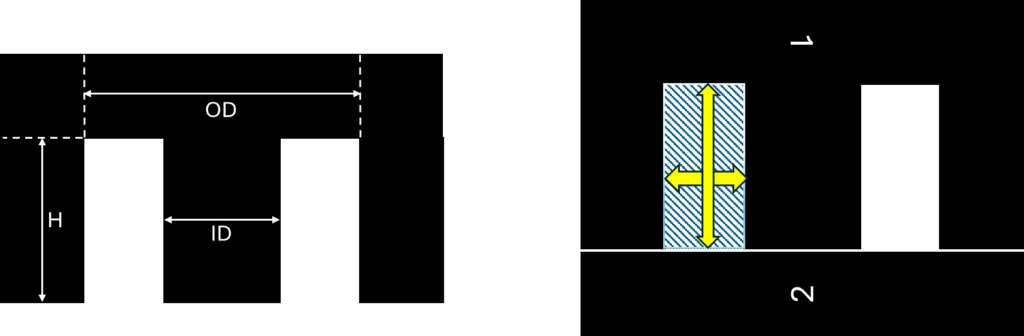
This is also forms the rectangle shape of area for winding. Hence,
Width of core, (remains same as EE core)
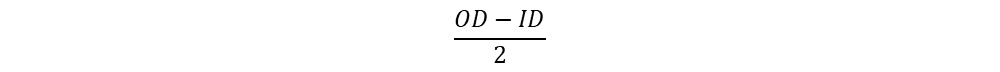
Height of core, ( half of EE core)
H
Window area of EI shape core:
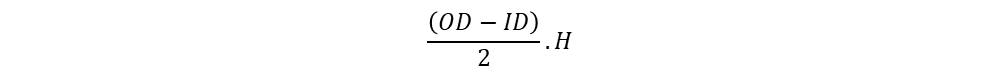
Therefore, overall EI shape window area becomes half of EE shape core due to height.
UU Core
In this, two U shapes connect together to close the path same like EE core shape
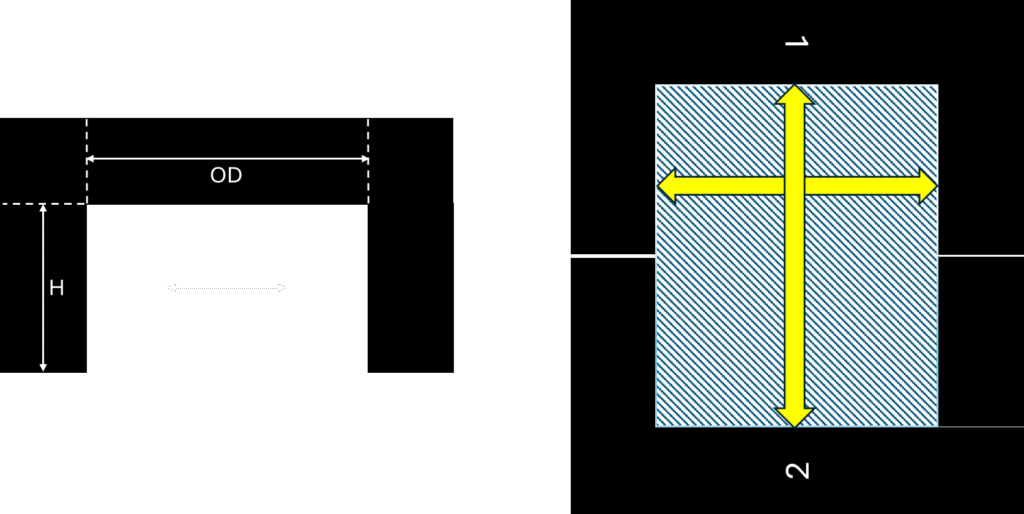
Width of core,
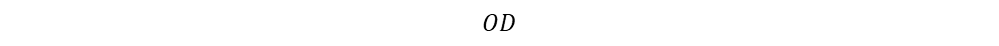
Height of core,
2H
Window area of UU shape core:
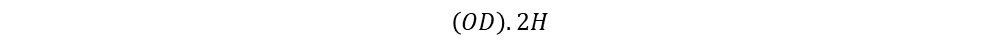
UI Core
We seen that, EI shape core area becomes half of EE shape core area. In similar passion, UI shape core area also becomes half of UU shape core area.
Width of core,
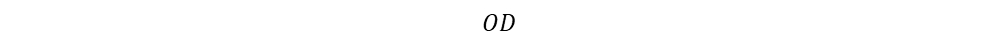
Height of core,
H
Window are of UI shape core:
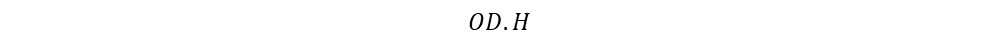
Toroidal Core
Toroidal means round shape. This shape is mostly used in inductor design but also can be used in transformer designs.
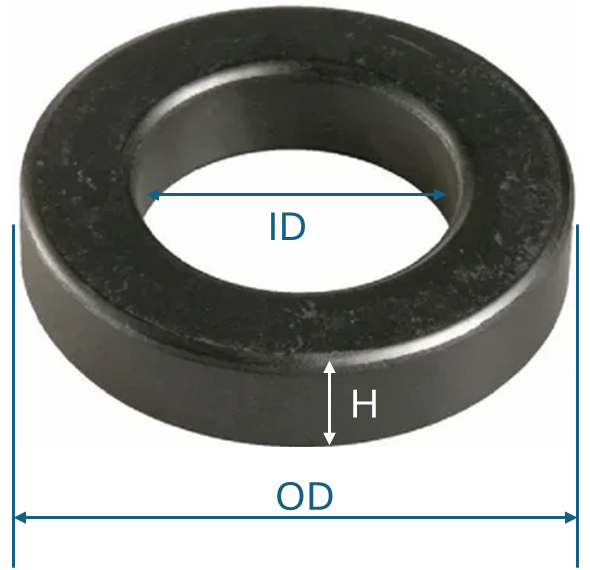

Here, entire inner diameter (ID) can be used for winding the wire.
Width of core,
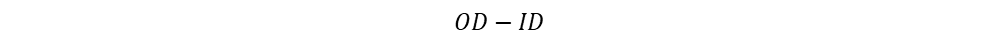
Height of core,
H
Window area of toroidal core:
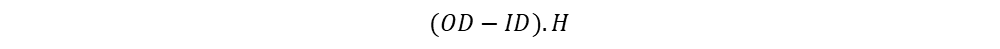
Parallel Cores
Sometimes we place the cores in parallel and wind on it for higher power applications.
When cores are connected in parallel like below passion and wind on it, there is no change in window area since no change of width and height. But, the cross sectional are of core multiplies how many cores are placed in parallel
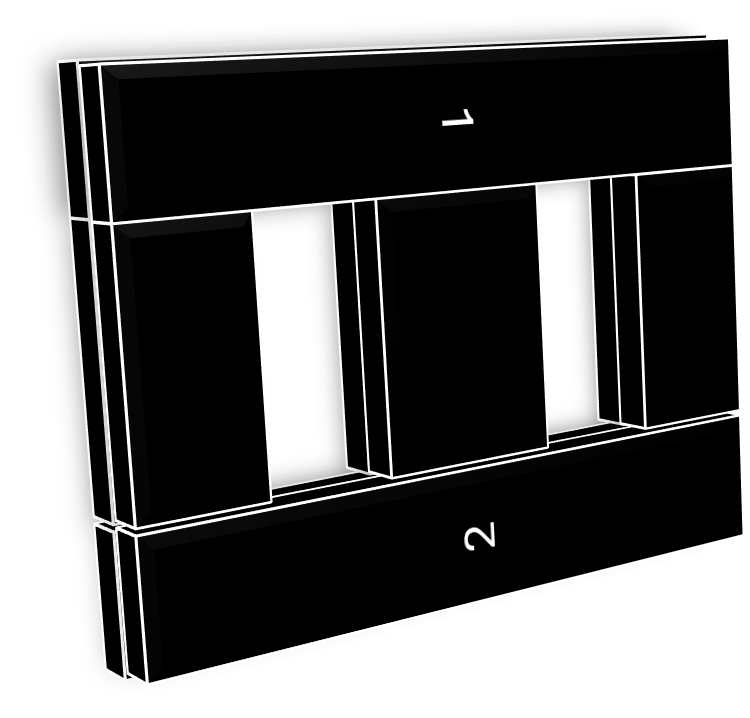
For example, if ‘n’ cores are placed in parallel,
AW(new) = AW
AE(new) = n AE
The summarized details of window area and cross-sectional areas for various core shapes are given below in table format for quick reference.
| Core shape | Window Area (AW) | Cross-sectional Area (AE) |
|---|---|---|
| EE | (OD-ID) . H | AE |
| EI | ((OD-ID)/2) . H | AE |
| UU | OD . 2H | AE |
| UI | OD . H | AE |
| Toroidal | (OD-ID) . H | AE |
| Paralleling (n-cores) | AW | n . AE |
Leave a Reply