DC-DC converter:
The converters which takes DC and it steps-up or steps-down that DC value in same form. If it steps-up the input voltage is called step-up DC-DC converter. If it steps-down the input voltage is called step-down DC-DC converter.
The power generation of renwable energy sources like solar are vary in nature due to these are depends on atmospheric condictions. To control and convert this power to an useful power, DC-DC converter is must.
Based on switching operation, DC-DC converters are classified into
- Hard-switching Converters
- Soft-switching Converters
Hard-switching Converters
Hard-switching converters use the PWM control methods to turn-on and turn-off switches in the converter. When switch transition takes place from on to off or vice-versa, it exhibits the power loss due to both current and voltage exist at the same time (shown in area).
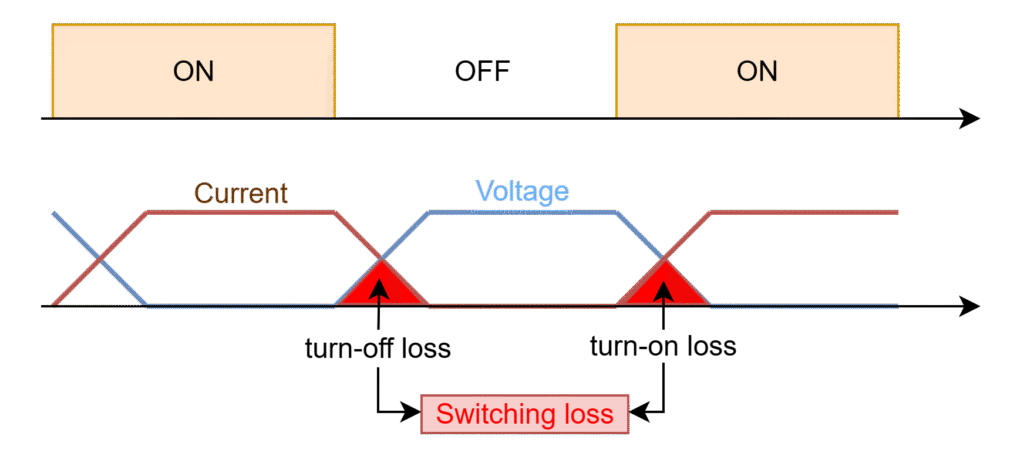
The power loss occurs at switch transistion from OFF to ON is called turn-on loss. The power loss occurs at switch transistion from ON to OFF is called turn-off loss. The sum of turn-on loss and turn-off loss is called switching loss.
Switch turn-on or turn-off with switching loss is called hard-switching. The converter which exhibit the switches with hard-switching is called hard-switching converters. These type of converters are also called as PWM converters.
Soft-switching Converters
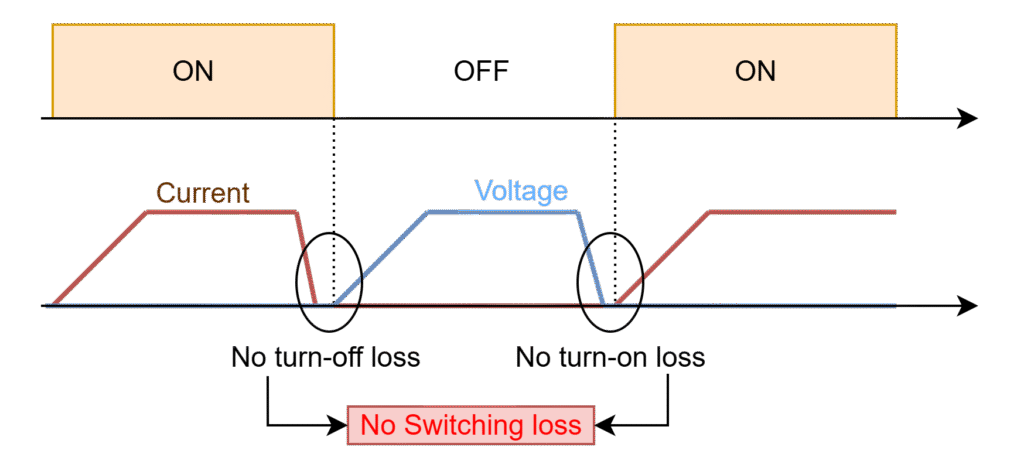
Soft-switching converters use the resonance control methods to turn-on and turn-off switches in the converter. These resonance methods minimizes the switching losses as shown below.
The resonance/softswitching methods are
- Zero-voltage switching (ZVS)
- Zero-current switching (ZVS)
The resonant converters are designed with either ZVS or ZCS method to achieve zero turn-on losses or zero turn-off losses respectively. ZVS method reduces the switch voltage to zero before gate signal is applied, hence, switch starts conducting immediately after gate signal is available with zero voltage and current flowing through it. Due to this, turn-on switching losses are ZERO as shown in above figure. Similarly, ZCS method reduces the switch current to zero before its gate signal turned-off, hence, switch stops conducting immediatley after gate signal is removed with zero current and voltage across it. Due to this, turn-off switching losses are ZERO as shown in above figure.

Why Resonant DC-DC Converters?
The following features are essentials for any power electronic converter/system
- Size
- Safety
- Efficiency
Size: Decreasing the size of the system increases the power density
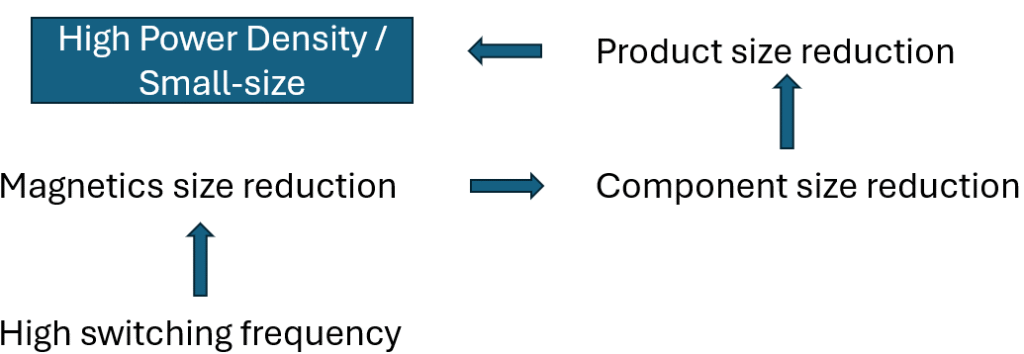
Increasing the switching frequency reduces the magnetics and component sizes. The overall product size reduced and improves the power density.
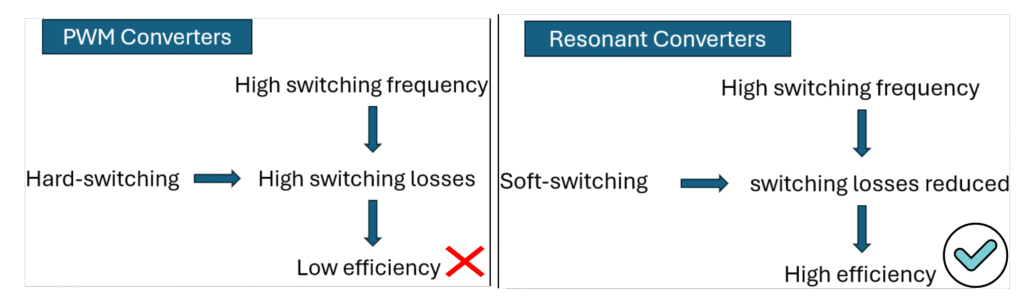
Due to soft-switching mechanisms, switching losses reduces even at high-frequency operations in the converter and then improves the efficiency of the converter in resonant converters.
Resonant Converters:
High-frequency operation
High power density
Low switching losses
High efficiency
Leave a Reply