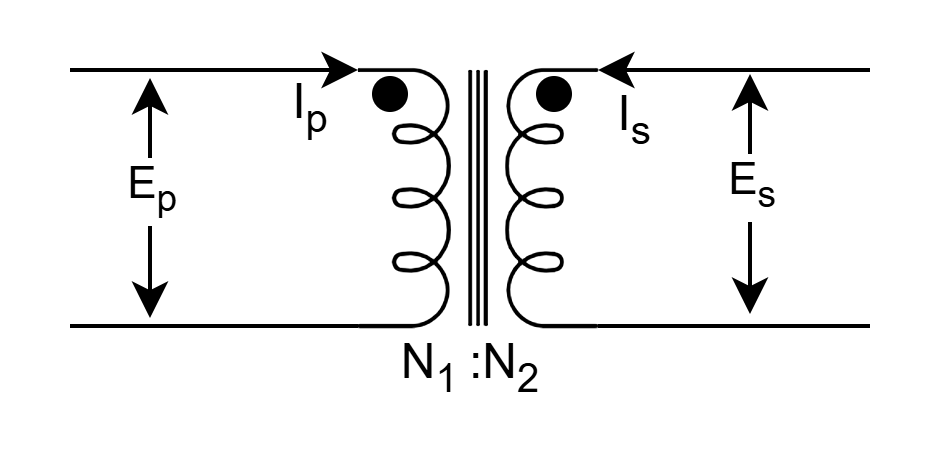
Area Product (AP) of core and number of turns (Np and Ns) for winding on core are two main equations which used in transformer desing procedure
Area Product (AP)
Area product is nothing but product of two areas, here in magnetics design, it’s a cross-sectional area and window area.
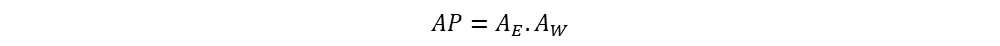
Current carrying conductor/wire is an electrical component and a magnet bar produces the magnetic field.
According to Faraday’s first law, placing the current carrying conductor in varying magnetic field (as shown in above figure), EMF (E) will induce.
That induced emf in a coil is equal to the rate of change of flux linkage as per Faraday’s second law. For ‘N’ number of turns, EMF is
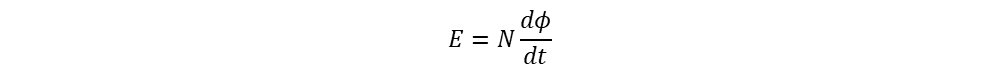
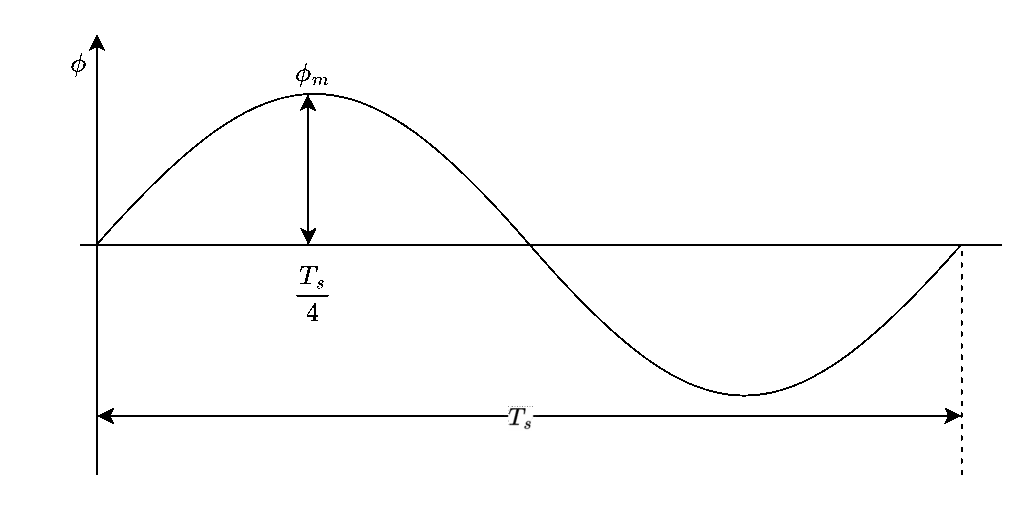
Consider a sinusoidal flux wave with time period ‘Ts’. The maximum flux occurs at 90o, that is Ts/4 of time period. Hence, the avergae EMF
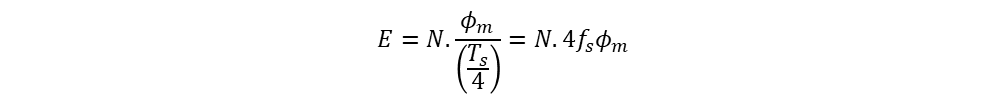
The RMS EMF is (Form factor x Avg ), a sinusoidal flux form factor is 1.11.
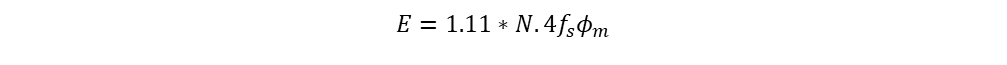
Total RMS of induced EMF in primary winding is
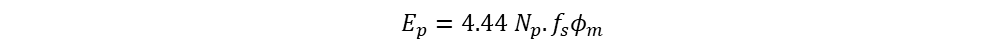
Flux is replaced with core material flux density and cross-sectional area
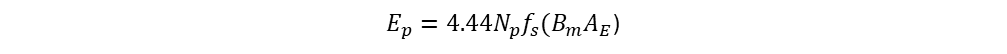
From above Equation, Cross-sectional area is
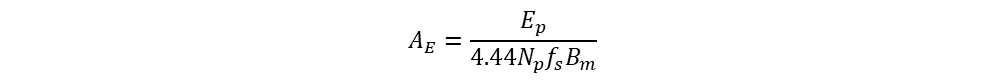
The current density in the transformer is same for both windings
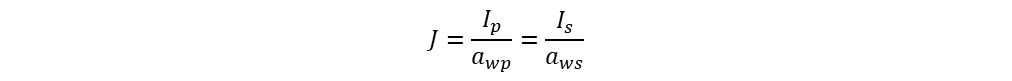
Also, ampere turns are equal
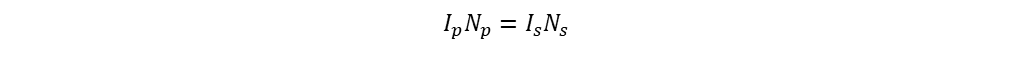
The total copper winding area is sum of primary and secondary winding copper areas
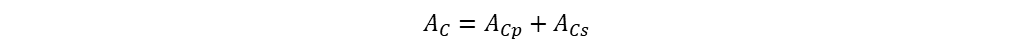
Copper area of winding is equal to total area of winding wire
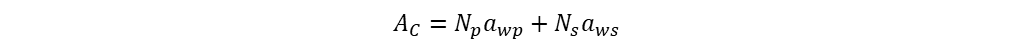
From the above all equations can achieve final equation for conductor copper winding area.
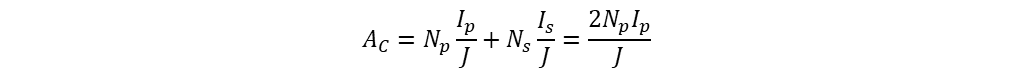
But copper area from core
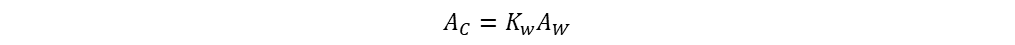
Therefore,
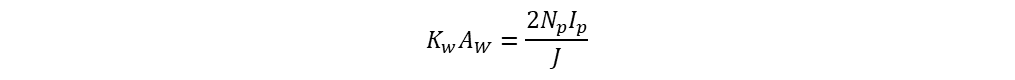
Window area is
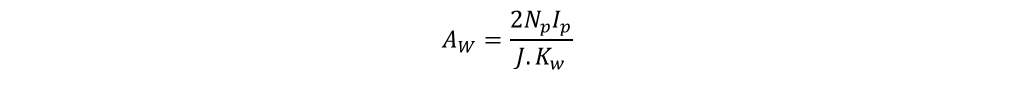
From two areas equations, area product is
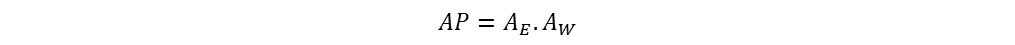
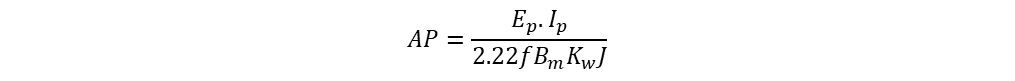
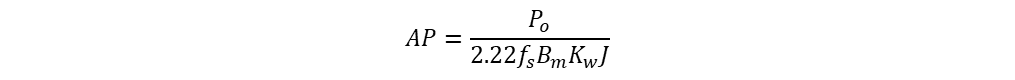
Number of turns (N1, N2)
From core data sheet, cross-sectional area is easily available.
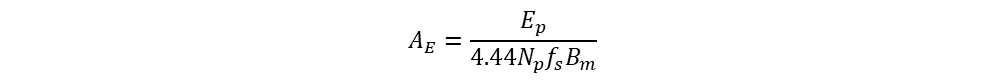
From above equation, primary winding number of turns
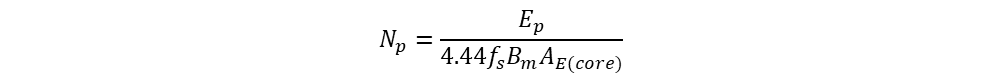
Here author considered a sinusoidal flux generation, hence form factor is 1.11. Lets check with different flux generation wavefroms here
Leave a Reply